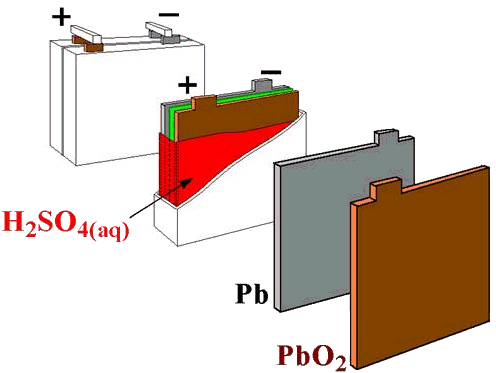
Chemistry
- There are two types plates in a charged battery: Pb and PbO2 (brown)
- The electolyte is 5-6 M H2SO4
- Both plates are converted to PbSO4(s) on discharging.
Therefore (LEARN)
- Pb → PbSO4(s) [Oxidation number of Pb changes from 0 to +2. Therefore lead is oxidised] Anode
- PbO2 → PbSO4(s) [Oxidation numbersof Pb changes from +4 to +2. Therefore lead dioxide is reduced] Cathode
for a lead acid battery being discharged.
From this basic structure the following half equations can be derived.
Anode/ oxidation: Pb + SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2e-
Cathode/ reduction: 4H+ + PbO2 + SO42- + 2e- → PbSO4(s) + 2H2O
Adding both equations
Pb + SO42-(aq) + 4H+ + PbO2 + SO42- + 2e- → PbSO4(s) + 2e- + PbSO4(s) + 2H2O
then simplify
The overall equation is
Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4 (aq) → 2 PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) Eo = 2 volts
A typical automobile battery consists of 6 cells in series and generates a total of 12 volts.
Hazards of recharging:
If a flat battery a re-charged too fast, hydrogen gas will be generated inside the battery as a side reaction.
2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g)
An internal spark may then cause the battery to explode and spray corrosive sulfuric acid into the face and body of a person. People have been blinded by this.
It is therefore strongly advised to re-charge flat batteries slowly overnight with a proper battery charger. This minimizes the production of hydrogen gas and also gives time for any hydrogen produced to dissipate.